Advanced SQL
Objectives
Describe the uses of advanced queries like subqueries and unions
Demonstrate ability to order data
Demonstrate ability to aggregate and combine data
Let's create some data tables that we can run some queries on. Go to a terminal and run psql. Create a new database named 'advanced':
CREATE DATABASE advanced;Now connect to it using \c advanced and create a new 'customers' table inside:
CREATE TABLE customers (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
age INTEGER,
country TEXT,
salary INTEGER
);Lastly, give it some data:
INSERT INTO customers (name, age, country, salary)
VALUES ('Bira', 32, 'Brazil', 2000);
INSERT INTO customers (name, age, country, salary)
VALUES ('Kaushik', 23, 'Kota', 2000);
INSERT INTO customers (name, age, country, salary)
VALUES ('Ramesh', 25, null, 1500);
INSERT INTO customers (name, age, country, salary)
VALUES ('Kaushik', 25, 'Mumbai', null);
INSERT INTO customers (name, age, country, salary)
VALUES ('Amelia', 27, 'England', 8500);
INSERT INTO customers (name, age, country, salary)
VALUES ('Silvana', null, null , 4500);You should be able to SELECT all the data and see this output:
Now let's make a friend for it. Create a new 'orders' table:
Give it some data:
Now SELECT * FROM orders; and you should see this table:
Order of SQL Clauses

Selecting Specific Data
It's great that we can select all records from a table but we frequently want to limit the results to a smaller set that meets some set of criteria. We saw the WHERE clause in the introduction to SQL lesson and saw how it can help us retrieve specific data. Here are a few more ways we can get more exclusive with our queries.
Remember that in SQL, our comparison operators are a little different. Equality is a single equals = and inequality is represented by a "greater-than-or-less-than" symbol <>.
COUNT()
COUNT() is an aggregate function.
"In database management an aggregate function is a function where the values of multiple rows are grouped together to form a single value of more significant meaning or measurement such as a set, a bag or a list." Read more on wikipedia.
We use an aggregate function to get the total count of customers in a table.
What about getting the count of something more specific in customer, such as the number of rows that have the age datapoint?
GROUP BY
GROUP BY is used to pull together identical data points. For example, say we just want to see the different ages we have in our customer table, without having to look through the duplicates too.
What if we just want to know how many different ages we have? We can combine GROUP BY and COUNT():
Or maybe we want the average salaries of the customers from each country:
Aliases
Aliases are a piece of a SQL query that allows you to temporarily rename a table or column for the current query.
Alter Table Command
Foreign Keys
Remember our 'orders' table:
That last column we defined is called a FOREIGN KEY. Foreign keys and primary keys are related in that a foreign key is basically a reference to a primary key in another table. In this case, we have a column in our 'orders' table called customer_id that references the primary key in the 'customers' table. This is the basis for making data relations with JOIN statements as we will see below. To summarize, the foreign key provides a sort of ownership link between the customer who has the primary key and all of that customer's orders in the related table where the customer_id matches the id from the 'customers' table.
Nested queries
What if I want to get names of customers with the highest salary.
Let's try it using WHERE
That will give us an error, because MAX is an aggregate function and can't be used in WHERE.
This will return the maximum rating, which we need to feed into WHERE.
Conditionals
CASE Statement
The CASE statement is used when you want to display different things depending on the data that you've queried from the database. There's two different ways to structure a CASE statement shown below. Note that in the first example you can only compare against single values while in the second example you can use actual expressions for evaluation. Also note that CASE statements require an ELSE statement.
JOINs
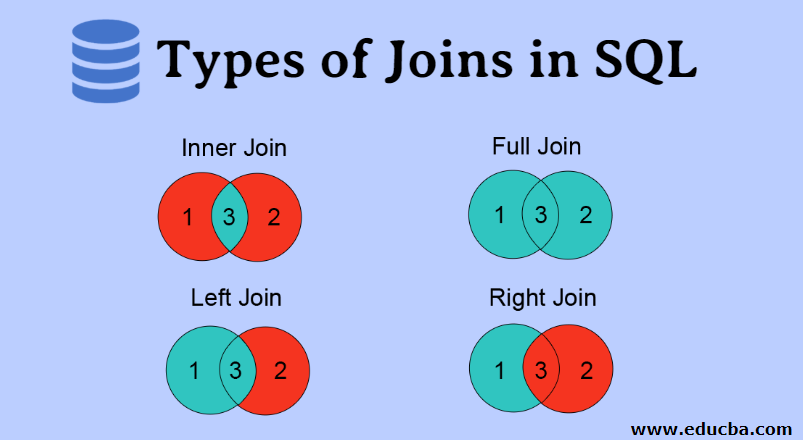
There are four types of JOINs in SQL:
LEFT JOINRIGHT JOININNER JOINFULL [OUTER] JOIN
Let's look at our table for customers and our table for orders. The customers table looks like this:
And the orders table looks like this:
As you can see, there are some customers who haven't placed orders. If we ask for the orders that correspond to customer_id 5, we will receive a value of NULL because they haven't ordered anything.
INNER JOIN
An INNER JOIN will return a dataset with all the matches from our customer and order tables where there is no NULL value on either side.
NOTE: This is the default type of JOIN so if you don't specify the type, SQL will perform an INNER JOIN.
FULL [OUTER] JOIN
NOTE: The OUTER is optional
A FULL OUTER JOIN will do the opposite of an INNER JOIN, returning you a table with all possible combinations, even if NULL has to be placed in.
TIP: The LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN below can both be considered types of outer joins
LEFT JOIN
With a LEFT JOIN the table returned will have all values in the left table, even if there is no corresponding value on the right side.
RIGHT JOIN
With a RIGHT JOIN the table returned will have all values in the right table, even if there is no corresponding value on the left side. This is a very rare join as it would require us to have orphaned records in the orders table. That is, orders that have no related customer. This is actually impossible with the way we have the tables set up. The foreign key constraint in the orders table basically says that you can't have a value in the customer_id column in the orders table if that id doesn't exist in the customers table. So when we run this, it looks exactly like our INNER JOIN above.
Unions
Unions display the results of two or more SELECT statements into one table, so the SELECT statements must have the same number of columns with the same names/data types, in the same order.
Here's a customers table:
and a subscribers table:
We could use this query to view the ids and names from both the customers and the subscribers tables.
Notice that the resulting table has fewer rows that the sum of the rows from each table. This is because UNION statements also eliminate any duplicate rows from the result. To include the duplicate rows, use UNION ALL.
Last updated