Filesystem Navigation
The file structure you see in the Terminal is the same as the one you see in the Finder application. Finder tends to hide some of the folders from you to keep things simple for most users, but everywhere that you go in Finder is accessible through the Terminal.
Common Navigation Commands
pwd- print working directoryopen- open a file/directoryls- list directory contentscd- change directory
pwd - Where am I?
pwd - Where am I?Wherever we are, pwd (short for print working directory) will show us what directory we are in.
pwd
/Users/romebellTypically the terminal will start in your HOME directory, each user has their own HOME directory, but on your computer it is common for you to be the only real user. At any given time a terminal shell process has one current working directory
open - Open a file/directory
open - Open a file/directoryopen .Wherever we are, open . opens a Finder window in the current directory. This can be handy for going between the terminal and Finder interfaces.
Additionally, we can open a file using the default application for the file.
ls - Listing directory contents
ls - Listing directory contentsWe can also list the files and directories in the current working directory. Your list may vary from the files/directories below.
Listing in the long format
To display this list in a cleaner format, we can pass options to the command. For example, the l option displays the list in a long format.
Now we can clearly see what files are in the current working directory. Some of these items are files, some are directories.
The ls command can take a directory as an argument
Listing hidden files
There's also a flag to list hidden files, which are files preceded with a period. These files are normally not visible in the command line unless we explicitly want them.
Using the a flag with ls will list hidden files. Note we can use flags in combination.
Hidden Files are typically used by applications to store configurations and there will be many of them in your home directory. Most users don't want to be editing these files so they don't show up in Finder, but you as a software developer will be editing some these for yourself.
Extra: The columns from the output of ls -la represent (from left to right)
type (
ddenotes a directory)file permissions
number of links (contained files and folders)
owner
group
file size
last modified data
file name
cd - Changing directories
cd - Changing directoriesWe can change directories by using the cd command, followed by the directory we want to change to. Let's try changing to the root directory.
We can verify that we are in the root directory by using pwd. Zsh also shows us the working directory.
Root Directory
The files and directories on your computer are structured in a tree. The 'top' of the file system is know as the root directory (That may sound upside down, but in our case the root is at the top :)
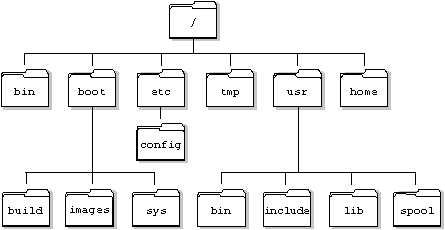
Home Directory
When logged in as a user, there will also be a home directory that represents your user's files. By default, the terminal will usually open in the home directory. As a shortcut, the tilde (~) can be used to change to the home directory. Just run cd ~.
Absolute and Relative Paths
Absolute Path
An absolute path is the full path written out from the root. For example, the full path of a file may look like this:
Navigating to this file would involve quite a lot of typing. Luckily, we can also use relative paths.
Relative Path
A relative path is a partial path relative to the current directory. For example, if Rome was already in /Users/romebell, a relative path for the file above would look like this:
Note that /Users/romebell was left off, because Documents/profile.png is relative to /Users/romebell.
We can also use relative paths to go back one or more directories.
Note that .. represents a link to the previous directory. The first command goes back one directory, and the second command goes back two directories. These are relative paths!
The third command doesn't take us anywhere. We can also use . to represent the current directory. Try it out to get used to these links.
Last updated