Display and Positioning
Display
Cool, right? Each HTML element gets its own box to live in.
As you saw, the outermost box of each element went all the way across the page. This is why, until now, your HTML elements have been sitting on top of one another: by default, they take up the full width of the page.
We can change all this with the first positioning property we'll learn, the display property and the four values we can use: inline, block, inline-block, and none.
--
Block Elements
by default, takes up the full width of the page
line break before and after
box model applies
examples:
Semantic block containers:
<div>,<main>,<section>,<header>,<footer>,<article>,<nav>,<aside>, etc.Text wrappers:
<p>,<h1>,...,<h6>,<blockquote>,<li>List containers:
<ul>,<ol>
Inline Elements
only takes up as much width as it needs
no line break before or after it
no box model
examples:
<img><a><span><em>,<strong>, etc.
Inline-Block Elements
only takes up as much width as it needs
no line break before or after it
box model!!!
If you assign none as the value of the display, this will make the element and its content disappear from the page entirely!
Here are a few examples in CSS, written as classes:
We would end up with something like this:

Play around with these different display options in this codepen.
Position
Another CSS property, "position", controls how the element appears related to other elements in the page flow. They are static, relative, fixed, and absolute
Static Positioning
HTML elements are positioned static by default. A "static positioned" element is always positioned according to the normal flow of the page and are not affected by the top, bottom, left, and right properties.
Again, the default positioning for all elements is static. This means that no positioning has been applied and the elements occurs basically where it appears in the document.
You rarely explicitly declare position:static like this because it is the default.
Relative Positioning
Declaring position:relative allows you to position the element top, bottom, left, or right relative to where it would normally occur.
When you adjust the top, right, bottom, or left props, you will move that side some distance from where it would have appeared by default
This is a common prop to use to tweak something just off of where it would normally be, for example to create a stylistic effect. However, this prop is also used in conjunction with absolute positioning as we will see below.
Fixed Positioning
An element with fixed position is positioned relative to the browser window. It will not move even if the window is scrolled, so a fixed positioned element will stay right where it is.
This is commonly used to make floating menus or buttons that stay on the page no matter how you scroll. This is how those dynamic "back to top" buttons are implemented.
Absolute Positioning
Specifying position: absolute will give you the ability to specify coordinates for where the element should go. It is important to know that this removes the element from the document flow and places it exactly where you tell it to be. This means that it can overlap or be overlapped by other elements. Absolute positioning will scroll normally with the page, unlike fixed positioning.
However, we must know what container we are absolutely positioning our element inside of. Absolute positioning will let us put our element at top: 10px and left: 14px, but of what? Where do these coordinates occur? The rule states that the absolute positioning occurs within the nearest positioned ancestor. When the browser finds an absolutely positioned element, it will look up the DOM tree to find a parent element that has the position property set to something other than static. When it finds one, the coordinates apply to that container and your element will be positioned inside that container's coordinate space. If it finds none, then your element will be absolutely positioned within the document body, meaning that the coordinate space is the entire browser view window.
Let's look at an example. Here we have a div container that we have given a position of relative. Note that this is all we need to do to start putting absolute positioned elements inside of it.

The relative positioning on the parent is what matters here. Below is what would happen if we forgot that:
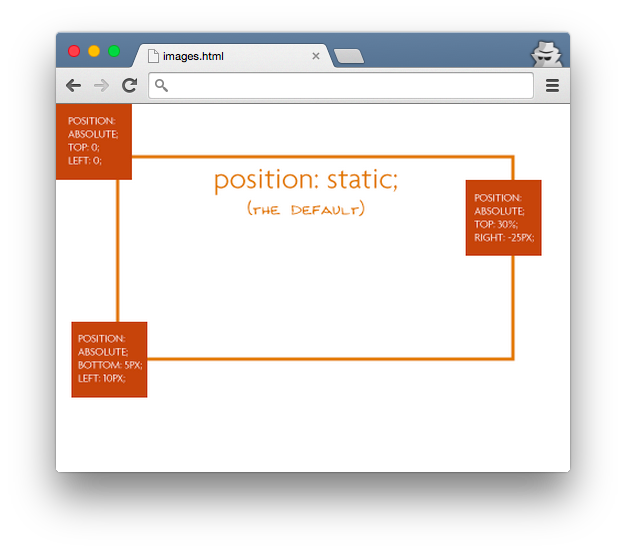
The "absolutely positioned" elements are positioning themselves in relation to the body element, instead of their direct parent. So if the browser window grows, that element in the bottom left is going to stick with the browser window, not hang back inside the div, like it was the case in the previous example.
There are many cases where you'll want to use absolute, but position an element exactly relative to another element. In that case, you can use absolute inside a relative element. See this Codepen for an example.
Check out this codepen to play around with these postion rules!
Last updated