Mongoose
Objectives
Update & destroy a model
Initialize & create a new instance of a model
Perform basic find queries
Reference other documents in an instance of a model
Work with embedded and referenced documents with Mongoose
MongoDB + Mongoose
Mongoose is to MongoDB as Sequelize is to a SQL database. But, because it maps code to MongoDB documents, it is referred to as an Object Document Mapper (ODM) instead of an ORM. Mongoose is going to make it easier to perform CRUD using object-oriented JS instead of working directly MongoDB.
Using the Mongoose ODM is by far the most popular way to perform CRUD on a MongoDB. Mongoose's homepage says it best:
"Mongoose provides a straight-forward, schema-based solution to model your application data"
Wait a second, what's with this "schema" business, isn't MongoDB schema-less? Well, yes it is, however, the vast majority of applications benefit when their data conforms to a defined structure (schema). Mongoose allows us to define schemas and ensures that documents conform.
Mongoose also provides lots of other useful functionality:
Default property values
Validation
Automatic related model population via the
populatemethodVirtual properties - create properties like "fullName" that are not persisted in the database
Custom Instance methods which operate on the document
Static methods which operate on the entire collection
preandpostevent lifecycle hooks (Mongoose "middleware")
The Big Picture
Here is the big picture overview of the components we'll be working with:
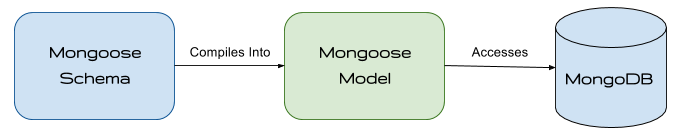
Big Picture Example
This is the general flow of how we will use Mongoose...
Make a Schema
What is a schema? It is just the structure of our data model: essentially the field names and what data type they are. This is similar the the schema we could see of each of our data tables in postgres. Viewing the table schema showed each of the columns and their data types. Recall that colmuns in SQL translate into fields or attributes in MongoDB.
We define the structure of our model as a schema...
This will make a single field named content and it will be a string.
Then we use this schema to build an actual model class...
This creates a model called Post (REMEMBER MODEL NAMES ARE ALWAYS SINGULAR). This two-step process results in a usable model similar to the ones we saw in Sequelize. It can be required and used to perform CRUD on the posts collection in the MongoDB:
Setting up Mongoose in your app
Create a new Express app and install the relevant npm packages:
To use Mongoose in your Node app:
With the package installed, lets use it - open index.js and setup your app:
You can now execute all the mongoDB commands over the database familyTree, which will be created if it doesn't exist.
Mongoose Event Handlers
Let's modify our index.js as follows:
We set up an event listener to fire once when the connection 'opens' to console log what host and port it is running on. It will also console log any errors whenever they occur.
Working with Models
Defining a Model
Like the ORMs we've worked with previously, Mongoose allows us to define models, complete with attributes, validations, and middleware (known as hooks in Sequelize). Let's make a model.
From within our family-tree app:
Now let's add:
MongoDB is schemaless, meaning: all the documents in a collection can have different fields, but for the purpose of a web app, often containing validations, we can still use a schema will cast and validate each type. Also note that we can have nested structures in a Mongoose model.
At the moment we only have the schema, representing the structure of the data we want to use. To save some data, we will need to make this file a Mongoose model and export it:
Notice that you can use objects and nested attributes inside an object.
Here's a look at the datatypes we can use in Mongoose documents:
String
Number
Date
Boolean
Array
Buffer (binary)
Mixed (anything)
ObjectId
Also, notice we create the Mongoose Model with mongoose.model. Remember, we can define custom methods here - this would be where we could write a method to encrypt a password.
Timestamps in Mongoose
Mongoose will add createdAt and add/update updatedAt fields if we set the timestamps option as follows in the schema:
Creating Custom Methods
When defining a schema, you can add custom methods and call these methods on the models. These are instance methods. Let's write a sayHello function under our schema:
Now we can call it by requiring the User model in index.js:
Now run the app with nodemon to see the result! You can define class methods in a similar manner by attaching the method to .statics instead of .methods
Interacting with MongoDB's CRUD
Let's hope into an interactive shell and test out CRUD functionality. To do this, from our app directory, we'll have to type in node and then require our Models manually.
Create
We can create a User using the .save method in Mongoose. You can also call .create to combine creating and saving the instance.
There is no "find or create" in Mongoose.
What about Read?
We can find multiple model instances by using the .find function, which accepts an object of conditions. There's also .findOne and .findById available.
Note that in the .find function, you can also use MongoDB queries such as $gt, $lt, $in, and others. Alternatively, there's a new .where syntax that can be used as well. Documentation on Model.where can be found here
Update
Models can be updated in a few different ways - using .update(), .findByIdAndUpdate(), or .findOneAndUpdate():
Destroy
Models can be removed in a few different ways - using .remove(), findByIdAndRemove(), and .findOneAndRemove().
Independent Practice
Using the code we just wrote and the official Mongoose Models docs, add three routes to your Express app.
GET users/, this will return all the documentsPOST users/, given some arguments in the url, this method will create auserrecord.DELETE users/:id, will remove the document corresponding to the collection
Last updated